Can a Car Accident Cause Tinnitus?
When you’re in a car accident that is someone else’s fault, you have a case for compensation. Valid claims include payments for emergency care and any follow up medical treatment you might receive. While some injuries, like cuts and broken bones, are easily tied to the incident, there can be “invisible” injuries that aren’t as easy to link to a crash.
Victims of car wrecks might suffer from conditions like tinnitus (ringing in the ears) as the result of an accident. Tinnitus has something in common with other injuries like neck pain or sciatica: Proving that a car accident was the cause can sometimes be tricky, as these conditions can also occur in other ways. Recognizing the symptoms and getting help right away is the key. With the proper evidence and the help of experienced car accident lawyers like these St Louis car accident attorney, you will be able to be fairly compensated.
Read More about: What Does “Pain And Suffering” Mean In A Car Accident Settlement?
What is Tinnitus?
According to the Mayo Clinic, tinnitus is the perception of sound in the ears that only the subject can hear. It’s most commonly described as ringing, but some people describe buzzing, roaring, clicking, chirping, hissing, humming, or whistling. It can show up in one or both ears and may be constant or intermittent.
Tinnitus is not actually a medical condition. Instead, it is a symptom of an underlying problem. It may be age-related or an indication of a disorder of the circulatory system. Most often, though, it results from acoustic trauma (exposure to loud noise) or an injury to the ear or head—all of which can happen in a car accident.
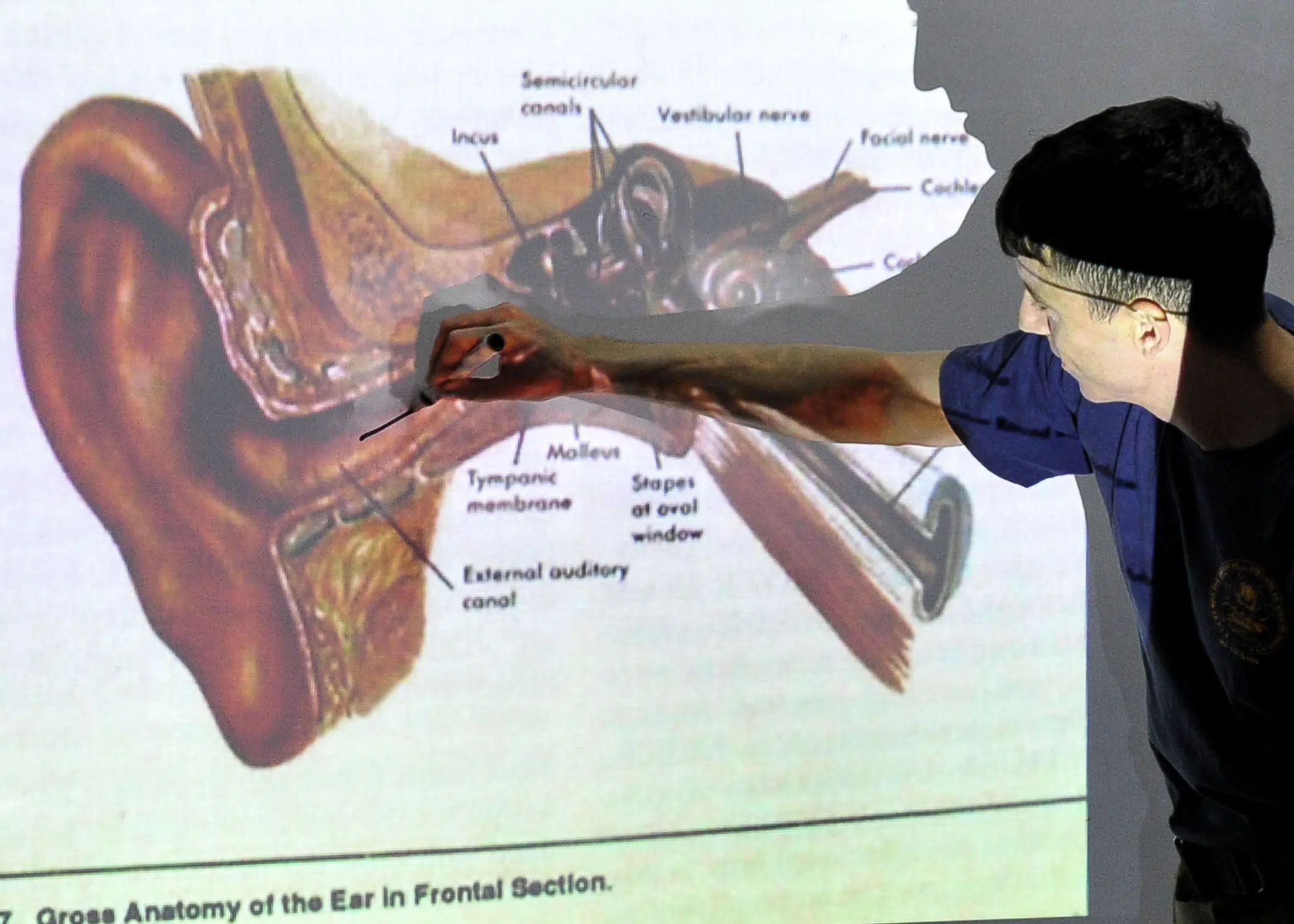
Ear damage might include a ruptured eardrum, fractures in the small bones of the ear, or auditory nerve damage. Blows to the head that result in traumatic brain injury can affect the hearing center of the brain. Tinnitus can be a symptom of any one of these problems.
Compared to other injuries, tinnitus may not seem significant. But any costs associated with its diagnosis and treatment should be included with any settlement or judgment that results from the car accident that caused it.
How Does a Car Crash Cause Tinnitus?
Car accidents can include loud noises and violent impact. Both can cause tinnitus. A decibel level of 120 to 140 is considered the “pain threshold” where ear damage can occur. An airbag explodes at 160 decibels of sound—comparable to a jet taking off. It’s no wonder that the loud bang of an airbag can make one’s ears ring.
And the impact of a crash can be very jarring to the body, even if there are no visible cuts or bruises. Whiplash happens when the head and neck are snapped forward with great force, like from a rear-end collision. And hitting the head during a wreck can produce anything from a sore “goose-egg,” to a concussion, to a traumatic brain injury.
Tinnitus might occur alongside any of these conditions. It should be discussed with the medical professionals who are addressing these other wounds.
How Serious is Tinnitus?
While tinnitus can sometimes accompany hearing loss, it is usually more bothersome than serious. It typically goes away after a few days or weeks, but in about 20% of all cases, it is permanent.
Some patients with tinnitus describe it as very distracting. It is sometimes loud enough to affect concentration or interfere with hearing other sounds. When the condition is temporary, this is merely a short-lived inconvenience. For those with permanent tinnitus, it can affect the overall quality of life.
Patients with chronic tinnitus often suffer from stress and fatigue. The condition can disrupt sleep patterns and interfere with concentration and memory. If it is associated with additional injuries to the inner ear, it can result in vertigo (dizziness and lack of balance).
Because tinnitus is only heard by the affected person, it is difficult to diagnose. Even so, it should be discussed with a doctor. A physician might refer a patient to an audiologist if there is concern that the tinnitus is connected to a more serious hearing issue.
There are no tests to confirm tinnitus, but there are some treatments for chronic cases. Most common are masking devices that attempt to replace the ringing with other sounds. Some people might get some relief simply by using radios or sound machines that produce “white noise.” In more serious cases, hear-aid type devices might be fitted to help mask the internal noise.
Read More about: 5 Things To Do Now If You Are In A Car Accident While Pregnant
How to Get Compensated
When tinnitus is caused by a car accident, the expenses for diagnosis and treatment should be reimbursed just like any other injury. There may be bills for doctor and audiologist visits, even if the condition is mild and subsides on its own. The patient deserves to be compensated for these costs when the accident was not their fault.
One factor that will help in proving that the tinnitus was caused by the accident is a physician’s notes on the subject. If you are in a car crash, it is important to disclose every single, ache, pain, and discomfort you are feeling. This should include ringing or other sounds in your ears as well as any difficulty hearing or concentrating. Each of these things could result in costly medical care—even if they turn out to be minor or temporary.
If these conditions do turn out to be serious or permanent, having documentation of them will be important to your case. These notes will verify that the condition exists and that it started when the car accident happened, you need a Belleville car accident lawyer.
Many people may dismiss a condition like tinnitus since it is usually minor and temporary. But it may stay around permanently and disrupt an accident victim’s life. Either way, victims deserve to be compensated for any money spent to check it out or treat it.
If you are in a car crash that is not your fault, read our list of the steps to take after a car accident. And contact Hipskind & McAninch. We’ll review your case and make sure you receive the support you need to move forward with your claim.
Category:
Car Accidents, Serious Injuries
Tags: